Reforming the Power Sector

Electricity (Amendment) Bill, 2025 aims at making the Indian industry and logistics more competitive by rationalising electricity cost and reducing hidden cross-subsidy
The government has unveiled the Electricity (Amendment) Bill, 2025, a major reform initiative aimed at overhauling the country’s electricity distribution sector, reducing systemic inefficiencies, and ensuring affordable, reliable power for consumers ranging from households and farmers to industries and logistics operators.
The Electricity (Amendment) Bill, 2025, is a major step toward transforming India’s power system to meet the needs of a rapidly growing economy. It aims to create a future-ready electricity sector that delivers reliable, affordable, and high-quality power to every consumer: farmers and households, to shops and industries.
The Bill moves away from the old monopoly supply model and encourages a performance-driven approach, where both public and private utilities compete fairly to improve consumer service. It promotes better use of the existing electricity network with transparency and accountability so that citizens get more value for every rupee spent.
Importantly, the reforms fully protect subsidised tariffs for farmers and low-income households. By providing a platform for the Centre and States to work together, it gives a big role to the states in shaping policies. More than just an update, this Bill is a blueprint for a modern, efficient, and resilient power sector. It aligns with India’s developmental aspirations, from farmers to industries. The bill supports the country’s vision of Viksit Bharat 2047, supporting India’s long-term economic growth.

The Electricity (Amendment) Bill, 2025, was brought forward to resolve deep-rooted inefficiencies, ease financial strain on the power sector, promote competition, and optimise network cost across India’s power distribution sector.
It was needed, because:
• Persistent financial losses in distribution companies (discoms) due to poor billing efficiency, high aggregate technical and commercial (AT&C) losses.
• Lack of competition in electricity supply, with consumers tied to a single discom, limiting service quality and innovation.
• Cross-subsidisation distortions, where industrial users pay inflated tariffs to subsidise other categories, making Indian manufacturing less competitive.
The Electricity (Amendment) Bill, 2025, aims to transform the existing market structure by rationalising cross-subsidy, promoting cost-reflective tariffs, and enabling direct procurement of power by industrial users. It seeks to dismantle longstanding barriers to India’s manufacturing competitiveness, making industrial power more affordable, reliable, and responsive to market demands, and at the same time protecting the subsidised tariff for farmers and other eligible consumers.
The Bill empowers State Electricity Regulatory Commissions (SERCs) to determine cost-reflective wheeling charges to ensure adequate network development by all the distribution licensees in accordance with the framework established by the SERCs. These regulated charges will be uniformly applicable to all users of the distribution network, whether public or private. This mechanism ensures that utilities have sufficient financial resources for staff salaries, routine maintenance, and future network development.
Powering Reform: Core Pillars of the Bill
The Electricity (Amendment) Bill, 2025, sets the stage for a more efficient, environmentally and financially sustainable, transparent, and consumer-focused power sector. It blends structural reforms with regulatory clarity to modernise electricity distribution across India. By aligning policy with evolving needs, the Bill aims to deliver quality service, financial discipline, and sustainable growth.
The Bill promotes fair competition between government and private distribution companies in electricity supply, overseen by State Electricity Regulatory Commissions (SERCs). This approach is expected to enhance service quality, boost operational efficiency, and offer electricity supply to the industrial sector at a reasonable cost. By shifting from a monopoly-based supply to performance-driven delivery, it fosters a more accountable and consumer-oriented power sector, while protecting the interests of the farmers and other consumers.
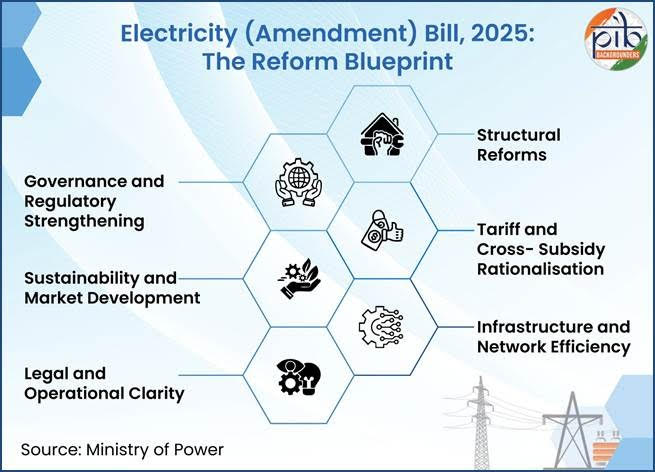
To sum up, the Electricity (Amendment) Bill, 2025, introduces key reforms to modernise India’s power sector. It promotes competition in distribution, strengthens regulatory oversight, and supports fair pricing mechanisms. The Bill safeguards subsidies for vulnerable consumers while enabling direct power access for industries. Together, these measures aim to build a more efficient, accountable, and future-ready electricity system aligned with national development priorities.